03 Dec 2024
Recently, the research paper titled "Sustainable human resource management and employee performance: A conceptual framework and research agenda" by Dr Xiaoyan Liang from the Department of Strategic Management and Organisation at the International Business School Suzhou (IBSS) of Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) has been accepted and published in the Tier 1* journal Human Resource Management Review. Dr Liang's research delves into the complex relationship between sustainable HRM practices and employee performance and offers an integrative framework to guide HR professionals in designing and implementing HRM practices that enhance employee performance and promote sustainable outcomes.

In the past two decades, sustainable human resource management (hereafter, sustainable HRM) has undergone rapid growth and development as a dynamic sub-field within human resource management, particularly since the inception of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. The COVID-19 pandemic further propelled interest in Sustainable HRM, with a surge in scholarly works exploring the intersection of the pandemic and sustainable workforce management.
Sustainable HRM embodies a comprehensive approach to managing employees that aligns with broader sustainability goals. It involves implementing HR strategies and practices aimed at minimizing negative impacts and fostering financial, social, and environmental objectives in a sustainable manner. Leading companies like SAP, Patagonia, and Unilever have been recognized for their innovative Sustainable HRM initiatives, such as social sabbaticals, environmental training, and sustainability education programs for employees.
Despite the progress, challenges persist in bridging the gap between theory and practice in Sustainable HRM, especially in understanding how these practices impact employee performance. Dr Liang’s study published in the Human Resource Management Review addresses this gap by investigating the complex relationship between Sustainable HRM practices and employee performance, through conducting a systematic literature review. Please see Figure 1 below for the synthesized findings.
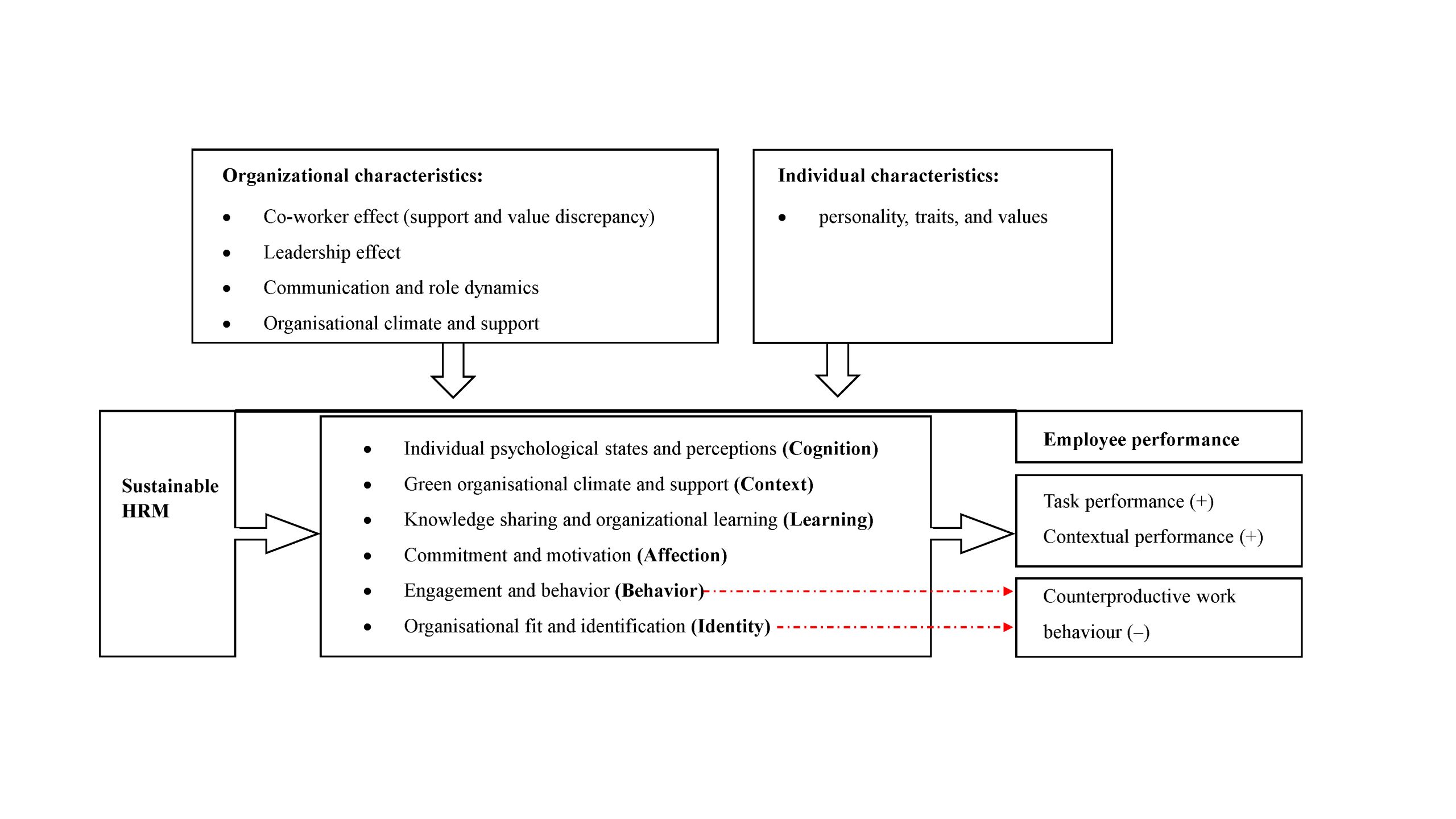
. An Integrated Framework of Sustainable HRM and Employee Performance: Mediators and Moderators
Source: Authors’ Own work
The study identifies six pathways through which Sustainable HRM practices can enhance employee performance: cognitive, contextual, learning, affective, behavioral, and identity pathways. In simpler terms, an organization’s sustainable HRM can affect employees’ performance if the organization first establishes connections with employees cognitively, affectively, or behaviorally, or enables identification, provides knowledge resources, or creates a favorable context. Social and cognitive psychology theories, useful for understanding how social interactions and cognitions shape individual behaviors, attitudes, and identities, have been largely deployed to explain these mediation mechanisms.
Dr Liang also identified individual and organizational characteristics as key moderators. Personal traits like conscientiousness and values such as environmental knowledge and commitment significantly influence how employees respond to SHRM practices. Organizational factors, including leadership style, organizational climate, and role dynamics, further refine how SHRM practices are internalized and expressed in employee performance.
The research offers a unified framework that integrates diverse perspectives on the impact of Sustainable HRM on employee performance. It also provides practical guidance for HR professionals to design and implement Sustainable HRM practices that resonate with employees and drive sustainable performance outcomes. By understanding the intricate relationship between Sustainable HRM and employee performance, organizations can foster a more sustainable and productive work environment for their employees.
Dr Xiaoyan (Christiana) Liang is an Assistant Professor at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU). Her research areas include Sustainable HRM, business ethics, CSR, corporate volunteer management and leadership. She has published in journals such as Asia Pacific Journal of Management, International Journal of Human Resource Management, Personnel Review, Journal of Global Information Management, Nonprofit Management and Leadership and others.
The Human Resource Management Review (HRMR) is a quarterly academic journal devoted to the publication of scholarly conceptual/theoretical articles pertaining to human resource management and allied fields (e.g. industrial/organizational psychology, human capital, labor relations, organizational behavior). It is listed as an ABS3, ABDC-A, CAS-Q1 journal, with an impact factor of 8.2.
03 Dec 2024