科研:EMC服务数据在JCR1区Nano Energy发表论文阅读次数 [2158] 发布时间 :2018-07-12 16:46:36
基于电镜中心(EMC)FEI电镜数据,深圳大学纳米所在JCR1区期刊Nano Energy上发表论文,具体如下:
Study on friction-electrification coupling in sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerator
Nano Energy,48(2018),456-463 (PDF-File)
Weiqiang Zhang, Dongfeng Diao*, Kun Sun, Xue Fan, Pengfei Wang*
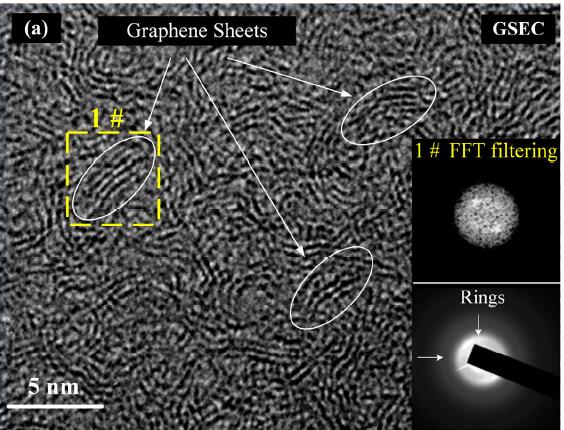
Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) is regarded as a revolutionary technology for harvesting clean and sustainable energy with low cost. Here, sliding-mode TENGs based on both graphene sheets embedded carbon (GSEC) and amorphous carbon (a-C) films were designed and their friction-electrification coupling properties were studied. The GSEC and a-C films were fabricated by electron irradiation assisted physical vapor deposition in an electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) plasma system. A novel testing platform that can simultaneously measure friction force, output voltage and output current was designed and assembled for studying the friction-electrification coupling of sliding-mode TENG. In the case of GESC and a-C films slid against Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film, the 5 open-circuit output voltage, the short-circuit output current density, the peak power density and the maximum instantaneous energy conversion efficiency were 13.5 V, 0.35 uA/cm2, 0.63 mW/cm2 and 8.61% for the GSEC film based TENG, and 8.5 V, 0.24 uA/cm2, 0.5 mW/ cm2 and 7.71% for the a-C film based TENG, respectively. The results implied that the GSEC film exhibited a higher electric output performance compared with the a-C film. The origin of high electric output performance of the GSEC film based TENG was ascribed to the edge and channel effects of graphene sheets. These findings shed light on the application of carbon films in friction-induced nanoenergy field.