
|
论文成果
当前位置: Chinese homepage >> 科学研究 >> 论文成果Metal-mediated nanobody assemblies as potent alleviators of human islet amyloid polypeptide aggregation
点击次数:
论文类型:文章
发表刊物:Materials Chemistry Frontiers
收录刊物:SCI
卷号:7
期号:10
页面范围:2068-2077
ISSN号:2052-1537
DOI码:10.1039/D2QM01372J
发表时间:2023-03-02
影响因子:8.683
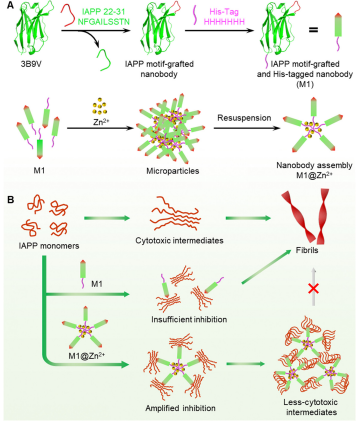
摘要:The misfolding and aggregation of peptides and proteins into β-sheet-enriched amyloid fibrils has been implicated in many human diseases. Inhibition of protein aggregation by engineered nanobodies has shown great promise in the treatment of amyloid-associated diseases. Taking type 2 diabetes associated human islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) aggregation as a model system, we generated a nanobody inhibitor by grafting the IAPP peptide fragment into the complementary determining region of a parent nanobody to inhibit IAPP aggregation through homotypic interactions. In addition, we developed a facile fabrication strategy to amplify the inhibitory effects of the designed nanobody inhibitor on IAPP aggregation. By coordinating a metal cation Zn2+ with a histidine-tag-fused nanobody inhibitor M1, the achieved nanobody assemblies M1@Zn2+ can significantly enhance the binding affinity between IAPP and M1 through the multivalent effects. At low substoichiometric concentrations (20 : 1 IAPP : nanobody molar ratio), M1@Zn2+ are capable of efficiently inhibiting IAPP aggregation, alleviating IAPP-induced cytotoxicity and downregulating ROS generation. This strategy represents an innovative attempt to design high-efficiency amyloid antibody inhibitors with enhanced therapeutic effects for the treatment of amyloid diseases.

